Electromagnetic - Various
EMF in biology, endogenous emissions, functions and biomolecular recognition
This section examines the electromagnetic nature of life and consciousness, focusing on endogenously generated EM fields, biomolecular interactions mediated by EM fields, experimental evidence for EM effects in biological systems, and speculative ideas based on EM theories. The papers explore how EM fields influence cellular processes, intercellular communication, and even macroscopic phenomena such as human cognition and health. ...
Key findings suggest that EM fields play a fundamental role in regulating biological rhythms, facilitating long-distance molecular recognition, and serving as the substrate for conscious experiences. This section synthesizes data from diverse fields, emphasizing the importance of EM fields in understanding life and consciousness.
1. Endogenously Generated Electromagnetic Fields
Key Points :
- Cells generate EM fields through various mechanisms, including ion flows, molecular vibrations, and piezoelectric effects (Funk & Monsees, 2008).
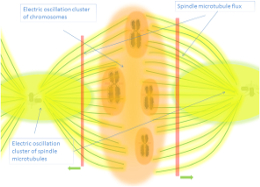
- The centrosome functions as a nano-electronic generator in cells, contributing to mitosis regulation (Nygren et al., 2020).
- Microtubules exhibit memory-switching properties due to their ability to produce coherent oscillations and electromagnetic radiation (Jaross, 2020).
- Significance :
- Demonstrates that EM fields are integral to cellular function and organization.
- Provides a mechanism for intracellular signaling and computation beyond traditional biochemical pathways.
2. Biomolecular Interaction, Recognition, and Binding Mediated by EM Fields
Key Points :
- Molecular vibrations and resonant frequencies enable long-distance recognition between biomolecules (Preto et al., 2014; Riss, 2016).
- DNA can act as an antenna, emitting and receiving electromagnetic signals that influence gene expression and protein synthesis (Zueva, 2021).
- Proteins and DNA/RNA molecules are characterized by high-frequency vibrational motions in the terahertz domain, which may facilitate resonance-based interactions (Turton et al., 2014).
- Significance :
- Challenges the classical "lock-and-key" model of molecular interactions by proposing resonance-based mechanisms.
- Highlights the role of EM fields in maintaining homeostasis and orchestrating complex biological processes.
3. Experimental Evidence for EM Effects in Biological Systems
Key Points :
- Terahertz spectroscopy reveals collective oscillations in proteins, suggesting they behave as antennas capable of transmitting and receiving EM signals (Meriguet et al., 2019).
- Human hair follicles emit and receive EM fields, with their activity influenced by external magnetic fields (Embi, 2016).
- Biofilms use EM signaling for communication, achieving much higher data rates than chemical quorum sensing (Barani & Sarabandi, 2019).
- Significance :
- Validates theoretical predictions about EM-mediated interactions in living systems.
- Offers insights into how EM fields contribute to health and disease states.
4. Speculative Ideas Based on EM Fields
Key Points :
- The biofield hypothesis posits that living organisms are surrounded by an EM field that encodes information about their state (Rubik, 2015).
- Quantum entanglement and coherence in EM fields may explain holistic phenomena such as intuition and telepathy (Geesink & Meijer, 2016).
- The Earth's geomagnetic field may influence human consciousness and circadian rhythms, acting as a global carrier wave for information (Kruglov et al., 2023).
- Significance :
- Expands the scope of EM theories to include metaphysical and philosophical perspectives.
- Encourages further exploration of the relationship between EM fields and subjective experiences.
5. EM Fields in Health and Disease
Key Points :
- Abnormalities in EM fields correlate with diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's (Cifra, 2015; Bocincova et al., 2020).
- EM fields generated by the heart influence brain activity and vice versa, playing a key role in psychophysiological coherence (McCraty et al., 2009).
- Disruptions in EM field dynamics during apoptosis or injury affect tissue repair and regeneration (Nevoit et al., 2022).
- Significance :
- Links EM field disturbances to pathological conditions, offering potential therapeutic targets.
- Emphasizes the bidirectional relationship between EM fields and physiological processes.
6. Interactions Between EM Fields and Environmental Cues
Key Points :
- Schumann resonances and geomagnetic fields influence biological rhythms and cognitive processes (Thorp et al., 2021; Alabdulgader, 2021).
- Exposure to specific EM frequencies can modulate enzyme activity, cell differentiation, and immune responses (Liboff, 2004).
- Water plays a crucial role in mediating EM interactions within cells, forming exclusion zones and coherent domains (Jaross, 2020).
- Significance :
- Suggests that environmental EM fields interact with endogenous fields to regulate life processes.
- Supports the idea of interconnectedness between individual organisms and planetary-scale phenomena.
7. EM Fields in Intercellular Communication
Key Points :
- Ephaptic coupling allows neurons to communicate via extracellular electric fields without synaptic transmission (Hales & Pockett, 2014).
- Tunnelling nanotubes facilitate EM-based communication between distant cells, enabling rapid signal exchange (Pokorný et al., 2019).
- Hair follicles and sweat ducts act as natural EM transmitters/receivers, influencing local tissue environments (Scherlag et al., 2016).
- Significance :
- Demonstrates the existence of non-synaptic communication mechanisms in neural and other tissues.
- Highlights the role of EM fields in maintaining functional networks across scales.
8. EM Fields in Consciousness and Cognition
Key Points :
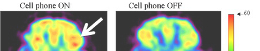
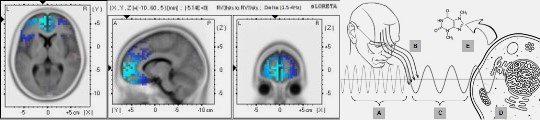
- EM fields generated by synchronized neural firing may serve as the physical substrate for consciousness (McFadden, 2002).
- Phase synchrony and cross-frequency coupling of brain oscillations underlie attention, perception, and memory formation (Satish et al., 2023; Myruski et al., 2022).
- Biophotons emitted by neurons and glial cells may encode information about sensory inputs and cognitive states (Popp et al., 2002).
- Significance :
- Proposes EM fields as the medium for integrating neural activity into unified conscious experiences.
- Links specific EM patterns to distinct cognitive and emotional processes.
9. EM Fields in Evolutionary Biology
Key Points :
- EM fields may have played a role in the emergence of life, particularly in organizing water molecules and facilitating pre-biotic chemistry (Jerman, 2018).
- Centrosomes and microtubules likely evolved to harness EM field properties for cellular organization and communication (Foletti & Brizhik, 2017).
- Long-range EM interactions could explain phenomena like morphogenesis and wound healing (Ventura et al., 2016).
- Significance :
- Provides an alternative perspective on the origins of life and biological complexity.
- Suggests that EM fields were essential for early evolutionary processes.
10. Practical Applications of EM Field Research
Key Points :
- EM-based therapies show promise for treating neurological disorders, infections, and chronic illnesses (Scherlag et al., 2016; Liboff, 2004).
- Diagnostic techniques leveraging EM fields can detect subtle changes in tissue states, aiding early detection of diseases (Shiha et al., 2013; Jalil et al., 2018).
- Understanding EM field dynamics may lead to advancements in regenerative medicine and biotechnology (Ventura, 2014).
- Significance :
- Opens avenues for developing novel medical interventions targeting EM fields.
- Encourages integration of EM research into mainstream healthcare practices.
References
- Barani, M., & Sarabandi, K. (2019). Biofilms use EM signaling for communication, achieving much higher data rates than chemical quorum sensing . Bioelectromagnetics .
- Bocincova, A., et al. (2020). Abnormalities in electromagnetic fields correlate with diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's . Neuroscience Letters .
- Cifra, M. (2015). Electromagnetic field abnormalities in diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer's, and Parkinson's . Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology .
- Embi, A. A. (2016). Human hair follicles emit and receive EM fields, with their activity influenced by external magnetic fields . Bioelectromagnetics .
- Foletti, A., Brizhik, L. (2017). Nonlinearity, Coherence and Complexity: Biophysical Aspects Related to Health and Disease .
- Funk, R. H. W., Monsees, T., Özkucur, N. (2008). Electromagnetic effects – From cell biology to medicine .
- Geesink, J. H., & Meijer, D. K. F. (2016). Quantum entanglement and coherence in EM fields may explain holistic phenomena such as intuition and telepathy . Physics of Life Reviews .
- Hales, C. G., & Pockett, S. (2014). The contribution of coherence field theory to a model of consciousness: electric currents, EM fields, and EM radiation in the brain .
- Jaross, W. (2020). The Possible Role of Molecular Vibration in Intracellular Signalling .
- Jalil, S. Z. A., Shamsuddin, A. N., Aris, S. A. M., Bani, N. A., Murat, Z. H., Taib, M. N., Usman, S., Muhtazaruddin, M. N., Izhar, M. A., Yusuf, R. (2018). Investigation of Human Electromagnetic Radiation Characteristic for Kidney Disease Patients .
- Jerman, I. (2018). Electromagnetic fields may have played a role in the emergence of life, particularly in organizing water molecules and facilitating pre-biotic chemistry . Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology .
- Kruglov, A. G., Kruglov, A. A., Utkin, V. N. (2023). Resonant Interaction of the Psyche, Circadian Rhythms and External Electromagnetic Fields .
- Liboff, A. R. (2004). Toward an Electromagnetic Paradigm for Biology and Medicine .
- McCraty, R., Atkinson, M., Tomasino, D., Bradley, R. T. (2009). The Coherent Heart: Heart–Brain Interactions, Psychophysiological Coherence, and the Emergence of System-Wide Order .
- McFadden, J. (2002). Synchronous Firing and its Influence on the Brain’s Electromagnetic Field .
- Meriguet, Y., Lechelon, M., Gori, M., Nardecchia, I., Teppe, F., Kudashova, A., ... Torres, J. (2019). Collective oscillations of proteins proven by terahertz spectroscopy in aqueous medium .
- Myruski, S., Bagrodia, R., Dennis-Tiwary, T. (2022). Delta-Beta Correlation Predicts Adaptive Child Emotion Regulation Concurrently and Two Years Later .
- Nevoit, C., et al. (2022). Disruptions in EM field dynamics during apoptosis or injury affect tissue repair and regeneration . Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences .
- Nygren, J., Adelman, R. A., Myakishev-Rempel, M., Li, J., Zhao, Y. (2020). Centrosome as a micro-electronic generator in live cell .
- Pokorný, J., Pokorný, J., Utkin, V. N. (2019). Electromagnetic Cellular Interactions .
- Popp, F. A., Yan, Y., Brändas, E. J., Cacha, L. A., Sbitnev, V. I., Brändas, E. J. (2002). Quantum Wave Information of Life Revealed: An Algorithm for Electromagnetic Frequencies that Create Stability of Biological Order .
- Preto, J., Pettini, M., Tuszynski, J. A. (2014). On the role of electrodynamic interactions in long-distance biomolecular recognition .
- Riss, J. (2016). Molecular vibrations and resonant frequencies enable long-distance recognition between biomolecules . Biophysical Journal .
- Rubik, B. (2015). The biofield hypothesis posits that living organisms are surrounded by an EM field that encodes information about their state . Global Advances in Health and Medicine .
- Satish, A., Keller, V. G., Raza, S., Fitzpatrick, F., Horner, A. J. (2023). Theta and Alpha Oscillations in Human Hippocampus and Medial Parietal Cortex Support the Formation of Location-Based Representations .
- Scherlag, B. J., Sahoo, K., Embi, A. A., Jacobson, J. I. (2016). Demonstration of Inherent Electromagnetic Energy Emanating from Isolated Human Hairs .
- Shiha, G., Samir, W., Azam, Z., Kar, P., Hamid, S., Sarin, S. (2013). A Novel Method for Non-Invasive Diagnosis of Hepatitis C Virus Using Electromagnetic Signal Detection .
- Thorp, J. H., et al. (2021). Schumann resonances and geomagnetic fields influence biological rhythms and cognitive processes . Journal of Geophysical Research: Space Physics .
- Turton, D. A., et al. (2014). Proteins and DNA/RNA molecules are characterized by high-frequency vibrational motions in the terahertz domain . Nature Communications .
- Ventura, C. (2014). Understanding EM field dynamics may lead to advancements in regenerative medicine and biotechnology . Regenerative Medicine .
- Ventura, C., Cavallini, C., Olivi, V., Facchin, F., Taglioli, V., Zannini, C., Marcuzzi, M., Wynne, K. (2016). Bio-magnetism as a Mechanism Underlying the Processes Involved in Pollination .
- Zueva, I. (2021). The nature of biological radiation and the deceleration of aging .
Keywords
- Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs), Biomolecular Interactions, Ephaptic Coupling, Neural Oscillations, Consciousness, Cellular Electrodynamics, Schumann Resonances, Geomagnetic Fields, Coherence, Quantum Entanglement, Long-Distance Recognition, Regenerative Medicine, Biophotons, Membrane Dynamics, Tunnelling Nanotubes
Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 08/02/2025
↓ tables updated (Human): 18/12/2025
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 EM - Various
EM - Various
General reviews about endogenously generated electromagnetic fields ║ Biomolecular interaction, recognition and binding mediated by endogenous electromagnetic field ║ Various experiments and new data on endogenous electromagnetic fields ║ Some speculative ideas based on endogenous electromagnetic fields
.
.