Electromagnetism & Resonant Recognition Model
The interaction between biomacromolecules is dependent of their electromagnetic resonant properties
The Resonant Recognition Model (RRM) offers a theoretical framework connecting electromagnetic (EM) frequencies with the biological functions of proteins and DNA. By identifying specific resonant frequencies associated with molecular interactions, RRM elucidates mechanisms underlying cellular communication, systemic coherence, and energy dynamics in biological systems. ...
This section synthesizes experimental evidence and theoretical developments, highlighting RRM’s implications for understanding molecular function, disease mechanisms, and therapeutic applications.
The Resonant Recognition Model, proposed by Irena Cosic, posits that biomolecules such as proteins and DNA emit and respond to electromagnetic frequencies linked to their primary sequences. This model is based on the periodic distribution of free electron energy along these molecules, enabling resonant energy transfer that governs molecular recognition and interaction. RRM has applications across various domains, from understanding protein functionality to exploring novel therapeutic avenues.
Key Principles of the Resonant Recognition Model:
Fundamental Concepts:
Proteins and DNA exhibit electromagnetic resonance determined by their primary sequence’s electron distribution.
Characteristic frequencies associated with biomolecular activity reflect the biological function and interaction of these molecules (Cosic et al., 1994).
Mechanism of Resonance:
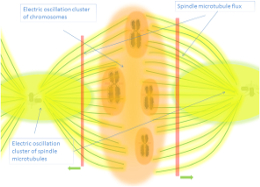
Electromagnetic fields mediate long-range molecular interactions, with resonant frequencies enabling precise molecular communication.
Frequencies are calculated using Electron-Ion Interaction Potential (EIIP) values, representing the energy distribution along biomolecular backbones (Faraji et al., 2022).
Experimental Evidence Supporting RRM:
DNA-Protein Interactions:
Studies show that DNA-enzyme interactions are facilitated by resonant electromagnetic frequencies, enabling interaction at significant distances (Faraji et al., 2022).
Bovine trypsin crystals irradiated with terahertz frequencies reveal structural changes consistent with RRM predictions.
Temperature and RRM:
Biological processes influenced by temperature, such as protein folding and enzymatic activity, align with RRM-derived frequencies (Cosic et al., 2020).
Specific frequencies, such as those involved in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) protein repair, illustrate the model’s applicability in genetic diseases (Cosic et al., 2019).
Light and Biophotonic Interactions:
RRM demonstrates that specific wavelengths of light stimulate cellular processes such as osteoblast differentiation, supporting applications in regenerative medicine (Paspaliaris et al., 2019).
Applications of RRM in Biology and Medicine:
Therapeutic Innovations:
RRM-guided electromagnetic fields have been shown to disrupt pathogenic interactions, offering potential in treating infections and cancer.
Frequencies within the visible light spectrum, particularly blue and green wavelengths, effectively stimulate protein activity (Cosic et al., 2016).
Understanding Disease Mechanisms:
RRM helps identify dysfunctional frequencies in disease-associated proteins, such as BRCA mutations in cancer pathways, enabling targeted interventions (Cosic et al., 2017).
Exploration of Biophoton Dynamics:
Biophotonic emissions correlated with RRM frequencies suggest a role in cellular signaling and energy transfer mechanisms.
Implications for Biological Coherence and Communication:
Biomolecules resonate with environmental and endogenous electromagnetic fields, integrating systemic coherence.
Solitonic and photonic interactions along biomolecular backbones facilitate efficient and precise energy transfer, critical for cellular coordination (Georgiev et al., 2013).
Understanding RRM’s principles bridges molecular biophysics and cellular biology, elucidating coherence mechanisms.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Standardizing methods for calculating and validating RRM frequencies remains essential for broader acceptance.
Interdisciplinary research integrating physics, biology, and medicine is critical for advancing RRM-based applications.
Expanding the database of experimentally validated RRM frequencies will enhance predictive accuracy and therapeutic relevance.
Conclusion: The Resonant Recognition Model provides a transformative lens for understanding molecular function and systemic coherence in biology. By linking electromagnetic frequencies with biomolecular activities, RRM unveils pathways for innovative therapies, deeper insights into disease mechanisms, and advancements in regenerative medicine. Future research promises to extend the boundaries of this model, solidifying its role in the intersection of biophysics and modern biology.
Keywords: Resonant Recognition Model, electromagnetic frequencies, molecular interaction, systemic coherence, biophotons, regenerative medicine, disease mechanisms.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 23/12/2024
↓ tables updated (Human): 29/04/2025
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 EM & Resonant Recognition Model
EM & Resonant Recognition Model
.
.