Biophotons - Various
Different roles of biophotons in communication and the health diagnosis by their measure
Biophotons, ultra-weak photon emissions generated by living organisms, play multifaceted roles in biological systems, ranging from intercellular communication to systemic regulation. Emerging evidence supports their coherence and functionality as carriers of biological information. ...
This section synthesizes data on biophotons from various systems, highlighting their roles in cellular communication, systemic health, ecological dynamics, and potential integration into broader electromagnetic frameworks. Additionally, it includes intriguing findings from recent studies, offering a comprehensive overview of their biological significance.
Biophotons represent a fascinating interface between quantum phenomena and biological processes. Generated by cellular and molecular mechanisms, these photons exhibit coherence properties akin to laser emissions, suggesting their role as precise information carriers. This section compiles evidence of their roles in cellular communication, coherence states, and broader biological applications. Additionally, unique findings from recent studies are discussed to underscore their broader biological implications. A perspective on their integration into electromagnetic frameworks is also presented.
Key Roles of Biophotons in Biological Systems:
Intercellular and Intersubject Communication:
Biophoton emissions facilitate non-chemical, non-contact communication within and between cells, supporting synchronized cellular responses across diverse tissues (Tong, 2024).
Studies on "bystander effects" demonstrate how irradiated cells emit biophotons that induce responses in non-irradiated neighboring cells (Mothersill & Seymour, 2019).
Biophotons enable long-range signaling in plants, coordinating systemic responses to environmental stress (Cifra et al., 2014).
Coherence Properties and Functional Implications:
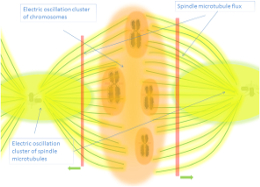
Biophotons exhibit quantum coherence, where their emissions are synchronized and phase-aligned, enabling efficient and rapid information transfer (Niggli, 2014).
DNA has been identified as a primary source of biophotons, acting as a repository for coherent light emissions (Popp, 2003). These emissions are hypothesized to regulate cellular processes and communicate genetic information.
Research indicates that biophoton coherence could be a hallmark of health, with disrupted coherence linked to pathological states such as cancer (Van Wijk et al., 2013).
Biophotons in Regulation and Homeostasis:
Biophotons interact with endogenous electromagnetic fields to maintain cellular and systemic coherence, particularly in stress and repair processes (Van Wijk et al., 2013).
Observations of biophotonic rhythms in humans suggest their synchronization with circadian and ultradian cycles, indicating their integration into systemic regulatory mechanisms (Zapata et al., 2021).
Studies on tissue repair reveal that biophoton emissions increase following injury, potentially acting as signals for regenerative processes (Hamouda et al., 2018).
Curious Findings from Recent Studies:
Biophoton Emissions in Reproductive Biology:
A study noted that human sperm emits biophotons during motility, with emissions increasing under oxidative stress. These emissions may provide insights into sperm quality and fertility diagnostics (Guo et al., 2020).
Biophoton rhythms in ovulatory cycles of mammals have been observed, suggesting a role in synchronizing reproductive behaviors in social species.
Temperature and Biophoton Emission Intensity:
Biophoton emission rates increase with temperature, reflecting metabolic activity. This has been leveraged in studying thermogenesis and metabolic health in small animals (Matsuhashi et al., 2019).
Biophotons in Microbial Communication:
Microorganisms, including bacteria, utilize biophotons for quorum sensing, a mechanism to regulate population density-dependent behaviors. This finding highlights a non-chemical mode of microbial communication (Fels, 2017).
Biophotons and the Electromagnetic Framework:
Photon-Based Communication in Neural Systems:
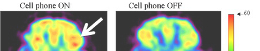
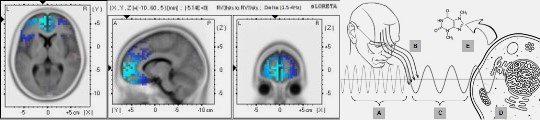
Neural tissues, particularly in the brain, are hotspots for biophoton emissions, correlating with neuronal activity and cognitive states (Van Wijk et al., 2010).
Studies propose that biophotons contribute to the brain’s information processing capabilities, complementing electrical and chemical signaling (Bókkon et al., 2018).
Emerging research links biophotons to quantum-like properties in neural systems, suggesting their involvement in phenomena such as decision-making and memory consolidation.
Integration with Broader Electromagnetic Frameworks:
Biophotons represent one modality of electromagnetic field (EMF) usage by biosystems. Their coherence properties align with the hypothesis that life organizes itself through interactions between various EMF frequencies (Tong, 2024).
EMF theories of cognition suggest that biophotons, alongside other endogenous fields, provide the substrate for a unified electromagnetic mind, with biophotons contributing unique quantum coherence features.
Biophotons may act as mediators between classical and quantum processes in biological systems, bridging scales of organization from molecules to cognition (Bischof, 2013).
Applications and Implications:
Diagnostics and Therapeutics:
Biophotonic emissions are emerging as non-invasive biomarkers for health monitoring, including cancer diagnostics and neurodegenerative disease tracking (Hamouda et al., 2018).
Therapeutic approaches leveraging biophotons, such as photobiomodulation, exploit their coherence properties to enhance cellular repair and systemic healing.
The use of biophoton-enhancing interventions, such as dietary antioxidants and structured water, has shown promise in modulating systemic health (Fels, 2017).
Ecological and Evolutionary Roles:
Biophotons are implicated in ecosystem regulation, mediating interactions across species and contributing to population dynamics (Fels, 2017).
Evolutionary perspectives posit that biophotons are an ancient signaling modality, conserved across diverse taxa for maintaining coherence and communication.
The adaptation of biophotonic emissions in nocturnal species suggests their role in low-light environmental navigation and predator-prey dynamics.
Discussion: Biophotons bridge molecular and systemic scales, serving as universal signals within a complex biological and electromagnetic network. Their coherence and quantum characteristics distinguish them as pivotal elements in cellular communication, systemic regulation, and ecological interactions. Recent findings on their roles in microbial communication, reproductive biology, and ecological health add depth to our understanding, offering novel perspectives on their evolutionary significance and practical applications. Furthermore, their integration into a broader electromagnetic framework provides a conceptual lens for understanding the intersection of biology and quantum fields.
Conclusion: The study of biophotons offers profound insights into the interplay of light and life. By framing biophotons as components of a larger biological and electromagnetic framework, this section highlights their potential to revolutionize our understanding of cellular communication, systemic regulation, and ecological interactions. Future research should explore their broader implications, with a focus on health diagnostics, environmental monitoring, and integration into electromagnetic theories of cognition.
Keywords: Biophotons, coherence, quantum biology, cellular communication, systemic regulation, microbial signaling, ecological health, electromagnetic frameworks, evolutionary biology.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 06/01/2025
↓ tables updated (Human): 17/01/2026
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 Biophotons - Various
Biophotons - Various
Reviews on Biophotons ║ Biophotons and intercellular or intersubject communication ║ Biophotons and blood ║ Biophotons differently emitted by cancer cells ║ Various experiments and new data on Biophotons ║ Some other theories/opinion on Biophotons ║ Biophotons in visual perception and imagery (Bókkon 's model)
|
|
|
|
| Author(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A |  | Humoral phototransduction: light transportation in the blood, and possible biological effects |  | 2008-(1) | F. Grass, S. Kasper |
| F |  | Biophoton research in blood reveals its holistic properties |  | 2003-(10) | V.L. Voeikov, R. Asfaramov, E.V. Bouravleva, C.N. Novikov, N.D. Vilenskaya |
| A |  | Ultra-weak chemiluminescence of smokers' blood |  | 1985-(1) | Binkoh Yoda, Yoshio Goto, Katsuro Sato, Akio Saeki, Humio Inaba |
.
.