Biophoton Sources
Experiments that give us more clues to recognize the possible origins of emissions
Biophotons, ultra-weak photon emissions from biological systems, have profound implications for understanding cellular communication and energy dynamics. Recent experimental evidence has solidified DNA as a primary source of biophotons, confirming earlier hypotheses by Popp and others. ...
This section synthesizes current findings on DNA-mediated biophoton generation, exploring its mechanisms, interactions with electromagnetic fields, and broader implications for biological coherence and systemic regulation.
Introduction: Biophotons, coherent ultra-weak photon emissions spanning ultraviolet to near-infrared wavelengths, are intrinsic to living systems. DNA’s unique structural and electromagnetic properties position it as a central player in biophoton generation. Groundbreaking studies have recently demonstrated DNA’s role as a source of biophotons, advancing our understanding of its functions beyond genetic storage. This section explores the evidence supporting DNA’s role in biophoton generation, its interaction with electromagnetic fields, and its implications for cellular communication and systemic regulation.
Mechanisms of DNA-Mediated Biophoton Generation:
Photon Emission from DNA:
DNA emits ultra-weak photons under physiological conditions, as shown in recent studies using genomic barley DNA (Pietruszka & Marzec, 2024).
Biophoton emission is linked to DNA’s fractal dimensions and entropy fluctuations, particularly under thermal and oxidative stress.
Photovoltaic and Resonant Properties:
DNA exhibits photovoltaic-like behavior, generating photoinduced currents in response to external stimuli (Pietruszka & Marzec, 2024).
These properties position DNA as a resonant cavity, capable of storing and emitting coherent light.
Biochemical Interactions:
Oxidative processes, such as those involving reactive oxygen species (ROS), contribute to DNA-mediated biophoton generation (Langer & Langer, 2023).
Proton flow and enzymatic reactions further modulate photon emission, supporting its role in energy transfer and cellular signaling.
DNA’s Interaction with Electromagnetic Fields:
Coherence and Energy Transfer:
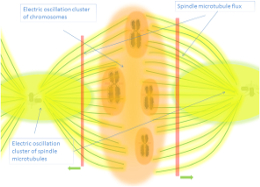
DNA’s helical structure enables coherent oscillations, facilitating resonant interactions with electromagnetic fields (Pietruszka & Marzec, 2024).
These interactions enhance biophotonic coherence, supporting cellular synchronization and systemic regulation.
Environmental Modulation:
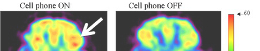
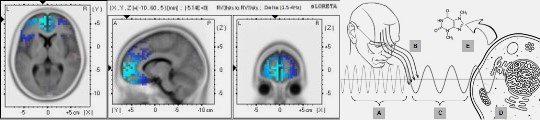
External EMFs, including natural frequencies like Schumann Resonances, influence DNA’s biophotonic activity, integrating environmental cues into biological systems.
Implications for Cellular Communication and Systemic Coherence:
Biophoton-Mediated Signaling:
DNA’s biophoton emissions act as carriers of information, coordinating intracellular and intercellular communication (van Wijk et al., 2010).
Biophotons enable rapid, non-contact signaling, aligning with quantum coherence theories.
Systemic Regulation:
DNA-driven biophotons contribute to circadian rhythms, energy metabolism, and developmental processes by modulating bioelectric fields.
These emissions integrate molecular activities with broader systemic functions, ensuring coherence across biological hierarchies.
Experimental Evidence and Advances:
Studies using advanced spectroscopy and interferometry have validated DNA’s role as a biophoton source (Pietruszka & Marzec, 2024).
Protonic and enzymatic contributions to biophoton emissions have been observed in mitochondrial and DNA systems, highlighting cross-organelle interactions in light emission (Langer & Langer, 2023).
Discussion: The recognition of DNA as a biophoton source revolutionizes our understanding of its role in biological systems. Beyond its genetic functions, DNA emerges as a key player in energy dynamics and cellular communication. Its interaction with electromagnetic fields underscores the integrative nature of biological coherence, linking molecular activities to systemic regulation. Future research should focus on the quantum biological mechanisms underpinning DNA’s biophotonic properties, advancing applications in diagnostics and regenerative medicine.
Conclusion: DNA’s role as a biophoton source highlights its multifaceted contributions to life, extending beyond genetic information storage to active participation in cellular communication and energy dynamics. These insights bridge molecular biology and biophysics, offering novel perspectives on life’s complexity and the integration of biological systems.
Keywords: DNA, biophotons, cellular communication, electromagnetic fields, oxidative processes, systemic coherence, quantum biology.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 26/12/2024
↓ tables updated (Human): 27/11/2024
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 Biophoton Sources
Biophoton Sources
.
.