High Frequency
Some possible therapeutic uses, including cancer treatment, of the few megahertz frequency range
High-frequency electromagnetic fields (HF-EMFs) exert diverse biological effects, including modulation of cell growth, inflammation, and systemic coherence. Recent studies reveal non-thermal mechanisms driving these interactions, such as membrane resonance and ion channel modulation, offering novel therapeutic avenues for conditions ranging from cancer to wound healing. ...
This section explores the mechanisms and systemic implications of HF-EMF interactions, emphasizing their role in cellular signaling, bioelectric modulation, and clinical applications.
Electromagnetic fields, particularly in high-frequency ranges, are increasingly recognized for their non-thermal biological effects. These fields modulate cellular and systemic processes, impacting everything from membrane dynamics to gene expression. This section synthesizes findings on HF-EMF interactions, exploring their mechanisms, biological effects, and therapeutic applications in oncology, tissue repair, and more.
Mechanisms of HF-EMF Interactions:
Non-Thermal Effects:
HF-EMFs induce non-thermal effects through mechanisms such as ion channel activation, membrane depolarization, and resonance phenomena (Wust et al., 2021).
Specific amplitude modulation enhances these effects, particularly in cancer cells, without causing thermal damage (Zimmerman et al., 2012).
Membrane Resonance and Ion Flux:
HF-EMFs resonate with membrane elastic properties, altering ion channel activity and calcium flux, which are critical for cellular signaling and metabolic regulation (Pilla et al., 2011).
Molecular Targets and Pathways:
Cellular membranes act as RF rectifiers, facilitating ion flux and triggering downstream biochemical cascades (Wust et al., 2021).
Biological Effects of HF-EMFs:
Cellular Modulation:
HF-EMFs affect cell proliferation and differentiation. For instance, fields at 27.12 MHz selectively inhibit tumor growth by targeting specific ion channels (Jimenez et al., 2018).
Modulation frequencies impact cellular signaling pathways, promoting tissue repair and reducing inflammation.
Tissue and Systemic Coherence:
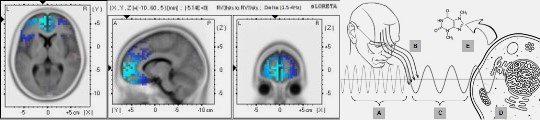
HF-EMFs enhance systemic coherence by aligning cellular bioelectric fields, supporting processes such as wound healing and immune regulation (Costantini et al., 2022).
Wound Healing and Inflammation:
Studies demonstrate accelerated keratinocyte migration and cytokine modulation under HF-EMF exposure, optimizing tissue repair and reducing inflammatory markers (Constantini et al., 2022).
Neurological and Cognitive Effects:
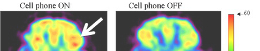
Low-intensity HF-EMFs at 64 MHz reduce amyloid-β levels in brain tissue, offering potential therapeutic pathways for neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s (Perez et al., 2021).
Therapeutic Applications:
Oncology:
HF-EMFs modulated at tumor-specific frequencies inhibit cancer cell proliferation and enhance differentiation, offering non-invasive therapeutic options (Zimmerman et al., 2012).
Emerging devices such as TheraBionic P1 show promise in improving survival rates in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma without significant side effects (Blackstock et al., 2021).
Pain Management and Regeneration:
Pulsed HF-EMFs improve postoperative pain and inflammation management, supporting recovery in orthopedic and reconstructive surgeries (Bianchi et al., 2018).
Plant and Microbial Applications:
HF-EMFs enhance nutrient absorption and growth in plant systems, demonstrating broader applications in agriculture (van Zyl, 2012).
Experimental Evidence and Advances:
Frequency-Dependent Effects:
Experimental data confirm that cellular responses to HF-EMFs depend on specific frequencies and amplitudes. For example, 13.56 MHz fields show anti-cancer effects, while lower frequencies enhance microbial growth (Ye et al., 2021).
Technological Innovations:
Advanced exposure systems allow precise modulation of HF-EMFs, optimizing therapeutic outcomes for diverse biological contexts (Jimenez et al., 2018).
Discussion: HF-EMFs represent a convergence of biophysics and medicine, highlighting the potential of electromagnetic modulation in cellular and systemic regulation. The evidence underscores the need for further research into frequency-specific effects, with implications for personalized medicine and integrative therapies.
Conclusion: High-frequency electromagnetic fields offer innovative solutions for medical and biological challenges. By leveraging their non-thermal mechanisms and systemic effects, HF-EMFs pave the way for advanced therapeutic strategies, enhancing health and disease management.
Keywords: high-frequency electromagnetic fields, non-thermal effects, bioelectric modulation, cancer therapy, wound healing, cellular signaling, systemic coherence.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 28/12/2024
↓ tables updated (Human): 17/10/2025
Applied Fields - Experimental
 High Frequency
High Frequency
|
|
|
|
|
| Author(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | Prophylactic Effects of Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field on Pulmonary Ischemia‐Reperfusion via HIF‐1α/eNOS Pathway and BCL2/BAX Signaling | 27.12 MHz - 0.026 mW/cm2 |  | 2025-(9) | Süleyman Emre Akin, Halil Asci, Muhammet Yusuf Tepebasi, İlter Ilhan, Özlem Ozmen, Selçuk Comlekci, Rümeysa Taner, Hasan Ekrem Camas, Ayşegül Keklik, Rasih Yazkan | |
| F | Acute exposure to 27.12 MHz radiofrequency electromagnetic field disrupts blood-brain barrier integrity via eNOS activation and occludin down-regulation | 27.12 MHz - 0.026 mW/cm2 |  | 2025-(8) | Arzu Ulusoy, Halil Asci, Rumeysa Taner, Muhammet Yusuf Tepebasi, Ilter Ilhan, Pinar Karabacak, Selcuk Comlekci, Ozlem Ozmen | |
| F | Radiofrequency electromagnetic field ınhibits HIF-1 alpha and activates eNOS signaling to prevent intestinal damage in a model of mesenteric artery ischemia in rats | 27.12 MHz - 0.026 mW/cm2 |  | 2025-(12) | Eyyup Sabri Ozden, Mustafa Soner Ozcan, Ilter Ilhan, Muhammet Yusuf Tepebas, Rumeysa Taner, Dincer Uysal, Halil Asci, Selcuk Comlekci, Ozlem Ozmen | |
| F |  | Frequency-Dependent Antioxidant Responses in HT-1080 Human Fibrosarcoma Cells Exposed to Weak Radio Frequency Fields | 2-5 MHz - 0.02 mT |  | 2024-(23) | Hakki Gurhan, Frank Barnes |
| F |  | Pulsed Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields as Modulators of Inflammation and Wound Healing in Primary Dermal Fibroblasts of Ulcers | 27.1 MHz |  | 2024-(14) | Erica Costantini, Lisa Aielli, Giulio Gualdi, Manuela Baronio, Paola Monari, Paolo Amerio, Marcella Reale |
| F |  | Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields Cause Non-Temperature-Induced Physical and Biological Effects in Cancer Cells | 13.56 MHz |  | 2022-(20) | Peter Wust, Paraskevi D. Veltsista, Eva Oberacker, Prabhusrinivas Yavvari, Wolfgang Walther, Olof Bengtsson, Anja Sterner-Kock, Marie Weinhart, Florian Heyd, Patricia Grabowski, Sebastian Stintzing, Wolfgang Heinrich, Ulrike Stein, Pirus Ghadjar |
| F |  | Low-energy amplitude-modulated radiofrequency electromagnetic fields as a systemic treatment for cancer: Review and proposed mechanisms of action | 27.12 MHz (0.1 Hz - 150 kHZ modulated) - (SAR 0.0017 W/kg) |  | 2022-(12) | Jack A. Tuszynski, Frederico Costa |
| F |  | Evaluation of Cell Migration and Cytokines Expression Changes under the Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field on Wound Healing In Vitro Model | 27.1 MHz |  | 2022-(14) | Erica Costantini, Lisa Aielli, Federica Serra, Lorenzo De Dominicis, Katia Falasca, Pamela Di Giovanni, Marcella Reale |
| A |  | A Systematic Method to Explore Radio Frequency Non-Thermal Effect on the Growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae | 1 MHz, 3.16 MHz, 10 MHz - (SAR 0.0024 W/kg) |  | 2021-(1) | Duye Ye, Gabriel Cutter, Tom Caldwell, Sarah Harcum, Pingshan Wang |
| F |  | Safety and Efficacy of amplitude-modulated radiofrequency electromagnetic fields in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma | 27.12 MHz (0.1 Hz - 150 KHz modulated, tumor specific) - (SAR 0.001 W/kg (body)) |  | 2021-(13) | Arthur W. Blackstock, Al B. Benson, Masatoshi Kudo, Hugo Jimenez, Preeya F. Achari, Callum McGrath, Volker Kirchner, Lynne I. Wagner, Nathaniel S. O’Connell, Kathy Walker, Valerie K. Pasche, Ralph D’Agostino Jr., Alexandre Barbault, Boris Pasche |
| F | Non-thermal membrane effects of electromagnetic fields and therapeutic applications in oncology | - |  | 2021-(17) | Peter Wust, Ulrike Stein, Pirus Ghadjar | |
| F | Repeated electromagnetic field stimulation lowers amyloid-β peptide levels in primary human mixed brain tissue cultures | 64 MHz - (SAR 0.4-0.9 W/kg) |  | 2021-(13) | Felipe P. Perez, Bryan Maloney, Nipun Chopra, Jorge J. Morisaki, Debomoy K. Lahiri | |
| A |  | Pilot study on the therapeutic potential of radiofrequency magnetic fields: growth inhibition of implanted tumours in mice | 10 MHz - 0.002 mT |  | 2020-(1) | Jukka Luukkonen, Jonne Naarala, Jukka Juutilainen, Frank Barnes, Carlos F. Martino |
| A |  | Changes in the gene expression in mouse astrocytes induced by pulsed radiofrequency: A preliminary study | 0.48 MHz (pulsed) |  | 2020-(1) | Kumiko Tanabe, Shigeo Takashim, Hiroki Iida |
| F | Arabidopsis cryptochrome is responsive to Radiofrequency (RF) electromagnetic fields (plant) | 7 MHz - 0.002 mT |  | 2020-(8) | Maria Albaqami, Merfat Hammad, Marootpong Pooam, Maria Procopio, Mahyar Sameti, Thorsten Ritz, Margaret Ahmad, Carlos F. Martino | |
| A |  | Acceleration of germination and early growth of plant seeds by high frequency and low intensity alternating electric fields | 100 MHz - 0.0066-2.653 mW/cm2 |  | 2020-(1) | Sumihiro Koyama, Yasuyuki Tamura, Gen Ishikawa, Yoichi Ishikawa |
| F | Tumour-specific amplitude-modulated radiofrequency electromagnetic fields induce differentiation of hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting Ca v 3.2 T-type voltage-gated calcium channels and Ca 2+ influx | 27.12 MHz (SAR 0.001-0.035 W/kg (body) 0.156-0.352 W/kg (1g)) |  | 2019-(16) | Hugo Jimenez, Minghui Wang, Jacquelyn W. Zimmerman, Michael J. Pennison, Sambad Sharma, Trevor Surratt, Zhi-Xiang Xu, Ivan Brezovich, Devin Absher, Richard M. Myers, Barry De Young, David L. Caudell, Dongquan Chen, Hui-Wen Lo, Hui-Kuan Lin, Dwayne W. Godwin, Michael Olivier, Anand Ghanekar, Kui Chen, Lance D. Miller, Yijian Gong, Myles Capstick, Ralph B. D'Agostino, Jr, Reginald Munden, Philippe Merle, Alexandre Barbault, Arthur W. Blackstock, Herbert L. Bonkovsky, Guang-Yu Yang, Guangxu Jin, Liang Liu, Wei Zhang, Kounosuke Watabe, Carl F. Blackman, Boris C. Pasche | |
| F | Ca2+ and CACNA1H mediate targeted suppression of breast cancer brain metastasis by AM RF EMF | 27.12 MHz - (SAR 0.255 W/kg (brain)) |  | 2019-(15) | Sambad Sharma, Shih-Ying Wu, Hugo Jimenez, Fei Xing, Dongqin Zhu, Yin Liu, Kerui Wu, Abhishek Tyagi, Dan Zhao, Hui-Wen Lo, Linda Metheny-Barlow, Peiqing Sun, John D. Bourland, Michael D. Chan, Alexandra Thomas, Alexandre Barbault, Ralph B. D'Agostino, Christopher T. Whitlow, Volker Kirchner, Carl Blackman, Boris Pasche, Kounosuke Watabe | |
| F | Use of Pulsed Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Field (Prfe) Therapy for Pain Management and Wound Healing in Total Knee and Reverse Shoulder Prosthesis: Randomized and Double-blind Study | 27.12 MHz |  | 2018-(7) | Nicola Bianchi, Federico Sacchetti, Matteo Mordà, Carmine Citarelli, Rodolfo Capanna, Stefano Giannotti | |
| A |  | Repeated Electromagnetic Field Stimulation in Aging and Health | 64 MHz - (SAR 0.6 W/kg) |  | 2018-(1) | Felipe P. Perez, Jorge J. Morisaki, Joseph P. Bandeira |
| F | In-vitro analysis of Quantum Molecular Resonance effects on human mesenchymal stromal cells | 4-64 MHz |  | 2018-(17) | Sabrina Sella, Valentina Adami, Eliana Amati, Martina Bernardi, Katia Chieregato, Pamela Gatto, Martina Menarin, Alessandro Pozzato, Gianantonio Pozzato, Giuseppe Astori | |
| F | Resonant Radiofrequency Fields Damaging Saccharomyces Cerevisiae (yeast) [preprint] | 28 MHz |  | 2018-(3) | W. S. Dias, E. H. M. Liquer, L. C. Gontijo, T. A. Oakes, G. S. Dias, C. Marques, H. S. Chavez | |
| A |  | Amplitude-modulated radiofrequency electromagnetic fields target hepatocellular carcinoma stem cells through activation of Cav 3.2 T-type calcium channels | 27.12 MHz - (SAR 0.0002-0.001 W/kg) |  | 2018-(1) | Hugo Jimenez, Minghui Wang, Jacquelyn W. Zimmerman, Michael J. Pennison, Sambad Sharma, Ivan Brezovich |
| A |  | Biophysical control of the growth of Agrobacterium tumefaciens using extremely low frequency electromagnetic waves at resonance frequency (bacteria) | 10 MHz (1 Hz modulated) - 0.000669 mT |  | 2017-(1) | M. Ali Fadel, Reem H. El-Gebaly, Shaimaa A. Mohamed, Ashraf M.M. Abdelbacki |
| F | Pulsed electromagnetic fields in knee osteoarthritis: a double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial | 27.12 MHz (1000 Hz pulsed) |  | 2015-(8) | Gian Luca Bagnato, Giovanni Miceli, Natale Marino1 , Davide Sciortino, Gian Filippo Bagnato | |
| F |  | Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Reduce Postoperative Interleukin-1β, Pain, and Inflammation: A Double- Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study in TRAM Flap Breast Reconstruction Patients | 27.12 MHz (2 Hz pulsed) - 0.0042 mW/cm (SAR 0.001 W/kg) |  | 2015-(10) | Christine H. Rohde, Erin M. Taylor, Amanda Alonso, Jeffrey A. Ascherman, Krista L. Hardy, Arthur A. Pilla |
| F | Effect of Pulsed Electromagnetic Field (PEMF) on Infarct Size and Inflammation After Cerebral Ischemia in Mice | 27.12 MHz (2 Hz pulsed) - (SAR 0.04 W/kg) |  | 2014-(10) | Juan Carlos Pena-Philippides, Yirong Yang, Olga Bragina, Sean Hagberg, Edwin Nemoto, Tamara Roitbak | |
| F |  | Increases in microvascular perfusion and tissue oxygenation via pulsed electromagnetic fields in the healthy rat brain | 27.12-MHz (5 Hz pulsed) - 0.0095 mW/cm (SAR 0.04 W/kg) |  | 2014-(10) | Denis E. Bragin, Gloria L. Statom, Sean Hagberg, Edwin M. Nemoto |
| F |  | Inhibition of cellular proliferation and enhancement of hydrogen peroxide production in fibrosarcoma cell line by weak radio frequency magnetic fields | 10 MHz - 0.01 mT |  | 2014-(5) | Pablo R.Castello, Iain Hill, Frank Sivo, Lucas Portelli, Frank Barnes, Robert Usselman, Carlos F. Martino |
| F |  | The Effects of Non-Invasive Radiofrequency Treatment and Hyperthermia on Malignant and Nonmalignant Cells | 13.56 MHz |  | 2014-(12) | Steven A. Curley, Flavio Palalon, Kelly E. Sanders, Nadezhda V. Koshkina |
| F | Non-Thermal Radio Frequency Stimulation of Tubulin Polymerization in Vitro: A Potential Therapy for Cancer Treatment | - |  | 2014-(23) | John T. Butters, Xavier A. Figueroa, Bennett Michael Butters | |
| F |  | Spin Biochemistry Modulates Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production by Radio Frequency Magnetic Fields | 7 MHz - 0.01 mT |  | 2014-(9) | Robert J. Usselman, Iain Hill, David J. Singel, Carlos F. Martino |
| F |  | Targeted treatment of cancer with radiofrequency electromagnetic fields amplitude-modulated at tumor-specific frequencies | - |  | 2013-(9) | Jacquelyn W. Zimmerman, Hugo Jimenez, Michael J. Pennison, Ivan Brezovich, Desiree Morgan, Albert Mudry, Frederico P. Costa , Alexandre Barbault, Boris Pasche |
| F |  | Electromagnetic fields instantaneously modulate nitric oxide signaling in challenged biological systems | 27.12 MHz (2 Hz pused) - 0.0025 mT |  | 2012-(4) | Arthur A. Pilla |
| F |  | Radio Frequency Energy for Bioelectric Stimulation of Plants (ICR) [thesis] | 1-50 MHz (16 Hz modulated) - max. 0.005 mT |  | 2012- (207) | Pieter Johannes Jacobus van Zyl |
| F |  | Cancer cell proliferation is inhibited by specific modulation frequencies | 27.12 MHz - (SAR 0.034 W/kg) |  | 2012-(7) | J. W. Zimmerman, M. J. Pennison, I. Brezovich, N. Yi, C. T. Yang, R. Ramaker, D. Absher, R. M. Myers, N. Kuster, F. P. Costa, A. Barbault, B. Pasche |
| F |  | Treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with very low levels of amplitude-modulated electromagnetic fields | 27.12 MHz (100 Hz-21kHz modulated) - (SAR max. 2 W/kg (10g)) |  | 2011-(9) | F.P. Costa, A.C. de Oliveira, R. Meirelles, M.C.C. Machado, T. Zanesco, R Surjan, M.C. Chammas, M. de Souza Rocha, D. Morgan, A. Cantor, J. Zimmerman, I. Brezovich, N. Kuster, A. Barbault, B. Pasche |
| F |  | Electromagnetic fields as first messenger in biological signaling: Application to calmodulin-dependent signaling in tissue repair | 27.12 MHz (pulsed) - (SAR 0.0001 W/kg) |  | 2011-(10) | Arthur Pilla, Robert Fitzsimmons, David Muehsam, June Wu, Christine Rohde, Diana Casper |
.
.