Microwave
Experimentally applied microwave frequencies and their non-thermal effects on biosystems
Microwave electromagnetic fields (MW-EMFs) influence biological systems through both thermal and non-thermal mechanisms, impacting cellular communication, tissue repair, and systemic regulation. This section synthesizes experimental findings on MW-EMF interactions with biological systems, emphasizing their effects on cellular signaling, oxidative balance, and potential therapeutic applications in oncology, neuroprotection, and regenerative medicine. ...
Microwave electromagnetic fields, spanning frequencies from 300 MHz to 300 GHz, have garnered attention for their multifaceted effects on biological systems. While traditionally associated with heating effects, MW-EMFs exhibit significant non-thermal interactions that influence cellular and systemic functions. This section explores the mechanisms underlying MW-EMF interactions, experimental evidence of their biological effects, and their implications for innovative therapeutic applications.
Mechanisms of Microwave Interactions with Biological Systems:
Thermal and Non-Thermal Effects:
Thermal effects arise from energy absorption, increasing molecular motion and local temperatures (Perez et al., 2021).
Non-thermal effects involve resonance phenomena, ion channel modulation, and alterations in protein folding and cellular signaling (Kuznetsov et al., 2017).
Water Molecule Polarization and Coherence:
MW-EMFs polarize water molecules, enhancing structured water domains and influencing intracellular coherence (Avakyan & Baranova, 2022).
This modulation affects energy distribution, molecular collisions, and cellular hydration states.
Membrane and Protein Modulation:
MW-EMFs influence membrane potentials and ion transport, particularly affecting calcium channels and neuronal excitability (Hinrikus et al., 2018).
Protein aggregation and enzymatic activities are altered under specific MW-EMF exposures, impacting metabolic and regulatory processes (Ivanov et al., 2020).
Biological Effects of MW-EMFs:
Cellular Communication and Oxidative Stress Modulation:
MW-EMFs enhance intercellular communication by modulating biophotonic emissions and bioelectric signaling (Zeni et al., 2021).
Oxidative stress is mitigated through upregulated antioxidant activity, supporting cellular resilience (Korolev et al., 2022).
Tissue Repair and Regeneration:
Experimental studies demonstrate MW-EMF-induced acceleration of tissue repair processes, including keratinocyte migration and fibroblast proliferation (Guerriero et al., 2015).
Oncology and Anti-Cancer Applications:
Specific frequency modulations inhibit tumor growth by selectively disrupting malignant cell signaling pathways without harming healthy cells (Jimenez et al., 2018).
Therapeutic Applications:
Neuroprotection and Cognitive Enhancement:
MW-EMFs improve neuronal recovery and reduce amyloid-beta levels, offering therapeutic potential for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions (Perez et al., 2021).
Regenerative Medicine:
MW-EMFs stimulate stem cell differentiation and tissue regeneration, providing novel approaches to healing complex wounds and degenerative conditions (Hinrikus et al., 2018).
Anti-Microbial and Food Safety Applications:
MW-EMFs reduce bacterial viability, presenting opportunities for non-invasive sterilization and contamination control (Rodriguez et al., 2018).
Experimental Evidence:
Studies demonstrate frequency-specific effects of MW-EMFs, such as:
Enhanced protein synthesis and intracellular regeneration in metabolic syndrome models (Korolev et al., 2022).
Non-thermal disruption of protein aggregation and neuronal membrane potentials (Ivanov et al., 2020).
Modulated cytokine activity and immune responses in murine models (Glushkova et al., 2016).
Discussion: MW-EMFs represent a promising frontier in biophysics and medicine, combining non-thermal effects with systemic biological coherence. Their ability to modulate bioelectric and biochemical processes highlights potential applications across oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine. Future research should explore the interplay between MW-EMFs, structured water, and quantum coherence in biological systems.
Conclusion: Microwave electromagnetic fields influence biological systems through multifaceted mechanisms, offering innovative therapeutic possibilities. By integrating MW-EMFs into medical and industrial practices, we can harness their potential to enhance health, safety, and systemic coherence.
Keywords: microwave electromagnetic fields, non-thermal effects, tissue repair, bioelectric modulation, neuroprotection, regenerative medicine, biophotons, oxidative stress.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 30/12/2024
↓ tables updated (Human): 25/05/2025
Applied Fields - Experimental
 Microwave
Microwave
Various experimental findings on microwave electromagnetic field application ║ Radio electric asymmetric conveyer (REAC) technology for cellular differentiation ║ Some experimental application of radiofrequencies acting through "Rife" resonance
|
|
|
|
|
| Author(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F |  | Influence of Super-Low-Intensity Microwave Radiation on Mesenchymal Stem Cells (review) | - |  | 2025-(14) | Mikhail Yu. Artamonov, Felix A. Pyatakovich, Inessa A. Minenko |
| F |  | Brain Disease-Modifying Effects of Radiofrequency as a Non-Contact Neuronal Stimulation Technology (review) | - |  | 2025-(21) | Shulei Sun, Junsoo Bok, Yongwoo Jang, Hyemyung Seo |
| A |  | [The use of drinking mineral water and low-intensity electromagnetic radiation at an early stage of metabolic syndrome development (experimental study)] (in Russian) | 1 GHz - 0.001 mW/cm2 |  | 2022-(1) | Yu N. Korolev, L. A. Nikulina, L. V. Mikhailik |
| F |  | 2.4 GHz Electromagnetic Field Influences the Response of the Circadian Oscillator in the Colorectal Cancer Cell Line DLD1 to miR-34a-Mediated Regulation | 2.4 GHz - 0.011 mW/cm2 |  | 2022-(21) | Soňa Olejárová, Roman Moravčík, Iveta Herichová |
| F |  | Microwave radiations of environment: On the possibility of inhibition of malignant mitosis | - |  | 2022-(8) | S. V. Avakyan, L. A. Baranova |
| F |  | Quantifying Physiological Biomarkers of a Microwave Brain Stimulation Device | 2.4 GHz + 5.2 GHz (35 Hz modulated) - (SAR 0.838 W/Kg + 1.175 W/kg) |  | 2021-(16) | Iqram Hussain, Seo Young, Chang Ho Kim, Ho Chee Meng Benjamin, Se Jin Park |
| F |  | Evidence of bystander effect induced by radiofrequency radiation in a human neuroblastoma cell line | 1950 MHz (3G UMTS) - (SAR 0.3 W/kg) |  | 2021-(7) | Olga Zeni, Stefania Romeo, Anna Sannino, Rosanna Palumbo, Maria Rosaria Scarfì |
| A |  | [Action features of the low-intensity electromagnetic radiation at an early stage of development of the experimental metabolic syndrome induced by a diet high in carbohydrates and fats] (in Russian) | 1 GHz - 0.001 mW/cm2 |  | 2021-(1) | Yu N. Korolev |
| A |  | Influence of Weak Microwaves on Spatial Collision and Energy Distribution of Water Molecules | 2.45 GHz, 5.8 GHz - 0.0000026-0.026 mW/cm2 |  | 2020-(1) | Dezhi Gou, Kama Huang, Ying Liu, Hongxiao Shi |
| F |  | AFM Imaging of Protein Aggregation in Studying the Impact of Knotted Electromagnetic Field on A Peroxidase | 2.3 GHz - 0.000000001 mW/cm2 |  | 2020-(9) | Yuri D. Ivanov, Tatyana O. Pleshakova, Ivan D. Shumov, Andrey F. Kozlov, Irina A. Ivanova, Anastasia A. Valueva, Vadim Yu. Tatur, Mikhail V. Smelov, Nina D. Ivanova, Vadim S. Ziborov |
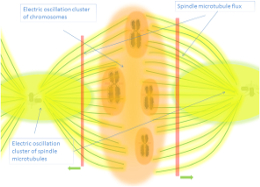
| A |  | Effect of microtubule resonant frequencies on neuronal cells | 91 MHz, 281 MHz, 3.0 GHz - 0.24 mW/cm2 (SAR 0.000012-0.00053 W/kg) |  | 2020-(1) | Yousef Rafati, Jody C. Cantu, Anna Sedelnikova, Gleb P. Tolstykh, Xomalin G. Peralta, Christopher Valdez, Ibtissam Echchgadda |
| A |  | Microwave pretreatment of tomato seeds and fruit to enhance plant photosynthesis, nutritive quality and shelf life of fruit | 9.3 GHz - (SAR 0.05-0.17 W/kg) |  | 2019-(1) | Shalini Verma, Vinay Sharma, Nilima Kumari |
| A |  | Effects of 171 MHz Low‐Intensity Electromagnetic Field on Glucocorticoid and Mineral Corticoid Activity of the Adrenal Glands of Rats | 171 MHz - 0.06-0.32 mW/cm2 |  | 2019-(1) | Sergey Perov, Nina Rubtsova, Quirino Balzano |
| F |  | The Effect of Repeated Electromagnetic Fields Stimulation in Biological Systems (water) | 50 MHz, 64 MHz, etc. - (SAR 0.4-0.6 W/kg) |  | 2019-(18) | Felipe P. Perez, James Rizkalla, Matthew Jeffers, Paul Salama, Cristina N. Perez Chumbiauca, Maher Rizkalla |
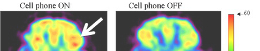
| F |  | A Clinical Trial of Transcranial Electromagnetic Treatment in Alzheimer's Disease: Cognitive Enhancement and Associated Changes in Cerebrospinal Fluid, Blood, and Brain Imaging | 915 MHz (217 Hz modulated) - (SAR 1.18 W/kg) |  | 2019-(26) | Gary Arendash, Chuanhai Cao, Haitham Abulaban, Rob Baranowski, Gary Wisniewski, Lino Becerra, Ross Andel, Xiaoyang Lin, Xiaolin Zhang, David Wittwer, Jay Moulton, John Arrington, Amanda Smith |
| A |  | Effects of Radiofrequency Exposure and Co-Expo-sure on Human Lymphocytes: the Influence of Signal Modulation and Bandwidth | 1950 MHz (CW & modulated) - (SAR 0.15-1.24 W/kg) |  | 2019-(1) | Stefania Romeo, Anna Sannino, Olga Zeni, Leopoldo Angrisani, Rita Massa, Maria Rosaria Scarfi |
| F |  | The Effect of Environmental Electromagnetic Radiation on Associate Formation in Aqueous Solutions (water)(microwave generation in ionosphere) | - |  | 2019-(7) | S. V. Avakyan, L. A. Baranova |
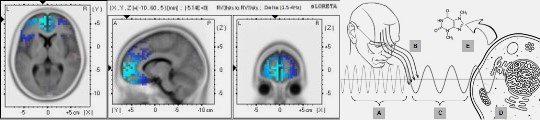
| A |  | Brain stimulation by modulated microwave radiation: a feasibility study | 450 MHz (40 Hz modulated) - 0.16 mW/cm2 |  | 2018-(1) | Maie Bachmann, Jaanus Lass, Andreas A. Ioannides, Hiie Hinrikus |
| F |  | Fas/FasL pathway and cytokines in keratinocytes in atopic dermatitis – Manipulation by the electromagnetic field | 900 MHz - 0.1 mW/cm2 (SAR 0.024 W/kg) |  | 2018-(12) | Lukasz Szymanski , Aleksandra Cios, Sławomir Lewicki, Pawel Szymanski, Wanda Stankiewicz |
| F |  | Use of non-ionizing electromagnetic fields for the treatment of cancer | - |  | 2018-(14) | Hugo Jimenez, Carl Blackman, Glenn Lesser, Waldemar Debinski, Michael Chan, Sambad Sharma, Kounosuke Watabe, Hui-Wen Lo, Alexandra Thomas, Dwayne Godwin, William Blackstock, Albert Mudry, James Posey, Rodney O’Connor, Ivan Brezovich, Keith Bonin, Daniel Kim-Shapiro, Alexandre Barbault, Boris Pasche |
| F |  | Non-Ionizing Electromagnetic Fields for Food Safety (in Spanish) | 2.41 GHz, 2.46 GHz |  | 2018-(8) | Arturo B. Rodriguez, Angélica Ganga, Liliana Godoy |
| F |  | Normothermic Microwave Irradiation Induces Death of HL-60 Cells through Heat-Independent Apoptosis | 2.45 GHz |  | 2017-(12) | Mamiko Asano, Satoshi Tanaka, Minoru Sakaguchi, Hitoshi Matsumura, Takako Yamaguchi, Yoshikazu Fujita, Katsuyoshi Tabuse |
| A |  | Breast cancer-specific amplitude modulated radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (AM RF EMF) inhibits brain metastasis of breast cancer | - |  | 2017-(1) | Sambad Sharma, Hugo Jimenez, Fei Xing, Carl Blackman, Boris Pasche, Kounosuke Watabe |
| A |  | Mechanism of Low-level Microwave Radiation Effect on Brain: Frequency Limits | 450 MHz (7-1000 Hz modulated) - (SAR 0.3 W/kg) |  | 2017-(1) | Hiie Hinrikus, Maie Bachmann, Jaanus Lass |
| A |  | Microwaves as a Skin Permeation Enhancement Method | - |  | 2017-(1) | Hamid R. Moghimi, Azadeh Alinaghi |
| F |  | Precision knockdown of EGFR gene expression using radio frequency electromagnetic energy | - |  | 2017-(8) | Ilya V. Ulasov, Haidn Foster, Mike Butters, Jae-Geun Yoon, Tomoko Ozawa, Theodore Nicolaides, Xavier Figueroa, Parvinder Hothi, Michael Prados, John Butters, Charles Cobbs |
| A |  | Epitaxy of the bound water phase on hydrophilic surfaces of biopolymers as key mechanism of microwave radiation effects on living objects (water) | - |  | 2017-(1) | Denis B. Kuznetsov , Ekaterina V. Orlova, Valery A. Neschislyaev, Igor L. Volkhin, Igor V. Izmestiev, Igor V. Lunegov, Alevtina V. Balandina, Dina G. Dianova |
| F |  | Evaluation of the Effect of Radiofrequency Radiation Emitted From Wi-Fi Router and Mobile Phone Simulator on the Antibacterial Susceptibility of Pathogenic Bacteria Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli | 900 MHz, 2.4 GHz - (SAR 0.13 W/kg & others ) |  | 2017-(8) | M. Taheri, S. M. J. Mortazavi, M. Moradi, S. Mansouri, G. R. Hatam, F. Nouri |
| A |  | Extremely low-level microwaves attenuate immune imbalance induced by inhalation exposure to low-level toluene in mice | 8.15–18 GHz - 0.001 mW/cm2 |  | 2017-(1) | Elena G. Novoselova, Olga V. Glushkova, Maxim O. Khrenov, Tatyana V. Novoselova, Sergey M. Lunin, Eugeny E. Fesenko |
| F |  | The role of p38 protein kinase in mouse responses to low-intensity electromagnetic radiation of the centimeter range | 8.15–18 GHz - 0.001 mW/cm2 |  | 2016-(7) | Olga V. Glushkova, Maxim O. Khrenov, E.V. Vinogradova, Sergey M. Lunin, Eugeny E. Fesenko, Elena G. Novoselova |
| F |  | Plant Responses to High Frequency Electromagnetic Fields (review) | (300 MHz–3 GHz) |  | 2016-(14) | Alain Vian, Eric Davies, Michel Gendraud, Pierre Bonnet |
| A |  | Mechanism of low-level microwave radiation effect on nervous system | 450 MHz (7, 40 & 1000 Hz pulse) - 0.16 mW/cm2 |  | 2016-(1) | Hiie Hinrikus, Maie Bachmann, Denis Karai, Jaanus Lass |
| F |  | Effectiveness of an Innovative Pulsed Electromagnetic Fields Stimulation in Healing of Untreatable Skin Ulcers in the Frail Elderly: Two Case Reports | 10.5 GHz (pulsed) 0.0000005–0.0001 mW/cm2 |  | 2015-(7) | Fabio Guerriero, Emanuele Botarelli, Gianni Mele, Lorenzo Polo, Daniele Zoncu, Paolo Renati, Carmelo Sgarlata, Marco Rollone, Giovannoi Ricevuti, Niccolò Maurizi, Matthew Francis, Mariangela Rondanelli, Simone Perna, Davide Guido, Piero Mannu |
| A |  | Inter-individual and intra-individual variation of the effects of pulsed RF EMF exposure on the human sleep EEG | 900 MHz (2 Hz pulse) - (max. SAR 2 W/kg (10g)) |  | 2015-(1) | Caroline Lustenberger, Manuel Murbach, Laura Tüshaus, Flavia Wehrle, Niels Kuster, Peter Achermann, Reto Huber |
| F |  | Microwave effect on diffusion: a possible mechanism for non-thermal effect (water) | 450 MHz - 0.160 mW/cm2 (SAR 0.4 W/kg) |  | 2014-(7) | Hiie Hinrikus, Jaanus Lass, Denis Karai, Kristjan Pilt, Maie Bachmann |
| F |  | Mobile Phone Radiation Alters Proliferation of Hepatocarcinoma Cells | 900-1800 MHz - (SAR 2 W/kg) |  | 2014-(9) | Elcin Ozgur, Goknur Guler, Gorkem Kismali, Nesrin Seyhan |
| F |  | Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria in Aqueous Media: Assessing the Potential of Real-Time Electromagnetic Wave Sensing | 2-10 GHz |  | 2014-(6) | I. Nakouti, O. Korostynska, A. Mason and A. I. Al-Shamma’a |
| F |  | Microwave absorption and permittivity of protein and microtubule solution | 0.2-50 GHz |  | 2014-(80) | Ondrej Krivosudský |
| F |  | Investigation of Antibacterial Effects of Electromagnetic Waves Emitted by Mobile Phones | 1800 MHz - (SAR 0.76 W/kg) |  | 2013-(6) | Ayhan Akbal, Hasan H. Balik |
| F |  | The role of the NF-κB, SAPK/JNK, and TLR4 signalling pathways in the responses of RAW 264.7 cells to extremely low-intensity microwaves | 8.15-18 GHz - 0.0014 mW/cm2 |  | 2014-(19) | Olga V. Glushkova, Maxim O. Khrenov, Tatyana V. Novoselova, Sergey M. Lunin, Svetlana B. Parfenyuk, Stanislav I. Alekseev, Eugeny E. Fesenko, Elena G. Novoselova |
| F |  | Effect of low power microwave radiation on pigment production in bacteria | 2.4 GHz (owen) |  | 2014-(5) | Shreya Raval, Vimla Chaudhari, Haren Gosai, Vijay Kothari |
| F |  | Effect of Low Power Microwave on Bacterial Growth, Protein Synthesis, and Intracellular Enzyme (Glucose-6-phosphatase and β-galactosidase) Activity | 2.4 GHz (owen) |  | 2013-(7) | Toshi Mishra, Preemada Kushwah, Vijay Kothari |
|
|
|
|
|
| Author(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F |  | REAC technology as optimizer of stallion spermatozoa liquid storage | 2.4-5.8 GHz |  | 2017-(12) | Fiammetta Berlinguer, Valeria Pasciu, Sara Succu, Ignazio Cossu, Sabrina Caggiu, Daniela Addis, Alessandro Castagna, Vania Fontani, Salvatore Rinaldi, Eraldo Sanna Passino |
| F |  | REAC technology modifies pathological neuroinflammation and motor behaviour in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model | 2.4 GHz |  | 2016-(12) | Luca Lorenzini, Alessandro Giuliani, Sandra Sivilia, Vito Antonio Baldassarro, Mercedes Fernandez, Matteo Lotti Margotti, Luciana Giardino, Vania Fontani, Salvatore Rinaldi, Laura Calzà |
| F |  | Radio Electric Asymmetric Conveyer: A Novel Neuromodulation Technology in Alzheimer’s and Other Neurodegenerative Diseases | 2.4-5.8 GHz |  | 2015-(4) | Salvatore Rinaldi, Laura Calzà, Luciana Giardino, Gabriele E. M. Biella, Antonio G. Zippo, Vania Fontani |
| F |  | Neurological morphofunctional differentiation induced by REAC technology in PC12. A neuro protective model for Parkinson’s disease | 2.4 GHz - 0,00004 mW/cm2 (SAR 0,00012 W/kg) |  | 2015-(8) | Margherita Maioli, Salvatore Rinaldi, Rossana Migheli, Gianfranco Pigliaru, Gaia Rocchitta, Sara Santaniello, Valentina Basoli, Alessandro Castagna, Vania Fontani, Carlo Ventura, Pier Andrea Serra |
| F |  | Stem cell senescence. Effects of REAC technology on telomerase-independent and telomerase-dependent pathways | 2.4 GHz - (SAR 0.00012 W/kg) |  | 2014-(8) | S. Rinaldi, M. Maioli, G. Pigliaru, A. Castagna, S. Santaniello, V. Basoli, V. Fontani, C. Ventura |
| F |  | Anti-senescence efficacy of radio-electric asymmetric conveyer technology | 2.4 GHz - (SAR 0.00012 W/kg) |  | 2014-(12) | Margherita Maioli, Salvatore Rinaldi,corresponding author Sara Santaniello, Alessandro Castagna, Gianfranco Pigliaru, Alessandro Delitala, Matteo Lotti Margotti, Luigi Bagella, Vania Fontani, Carlo Ventura |
| F |  | Radio Electric Conveyed Fields Directly Reprogram Human Dermal Skin Fibroblasts Toward Cardiac, Neuronal, and Skeletal Muscle-Like Lineages | 2.4 GHz - (SAR 0.00012 W/kg) |  | 2013-(7) | Margherita Maioli, Salvatore Rinaldi, Sara Santaniello, Alessandro Castagna, Gianfranco Pigliaru, Sara Gualini, Claudia Cavallini, Vania Fontani, Carlo Ventura |
.
.