Electromagnetism & Morphogenesis
Fields guiding the positioning of organelles in cells, cells in organs and organs in bodies
This section explores the role of electromagnetic fields (EMFs) in regulating morphogenesis and cellular behavior, focusing on experimental evidence and theoretical frameworks that support an electromagnetic theory of life. The listed papers highlight how EMFs influence developmental processes, tissue organization, and intercellular communication. ...
Key findings include the generation of coherent oscillations by centrosomes and microtubules, which guide cell division and differentiation, as well as the capacity of biofilms to use EM-based communication for long-range signaling. Additionally, the relationship between morphogenetic fields and consciousness is discussed as a side note, emphasizing how form and structure serve as the physical substrate for expressing life's "to be" quality.
1. Bioelectric Fields in Morphogenesis
Key Points :
- Bioelectric communication among cells plays a critical role in shaping tissues and organs (Manicka & Levin, 2025).
- Resting membrane potentials (Vmem) within tissues contribute to spatiotemporal patterns that regulate complexity, dimensionality, and causality (Levin, 2023).
- External electric fields can halt or reverse morphogenesis in organisms like Hydra, demonstrating the instructive role of EM fields in development (Braun & Ori, 2019).
- Significance :
- Provides mechanisms for how EM fields guide morphological processes.
- Links bioelectric dynamics with fundamental biological phenomena such as regeneration and cancer suppression.
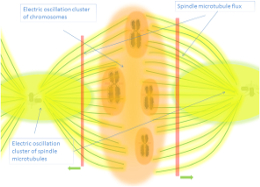
2. Centrosomes and Microtubules as EM Generators
Key Points :
- Centrosomes act as geometry organizers through their electrostatic properties, influencing cell orientation and division (Regolini, 2019).
- Microtubules generate electromagnetic waves and exhibit features of both synchronization and swarming, contributing to long-range intercellular communication (Pietak, 2012; Tuszynski, 2019).
- Mechanical buckling of microtubules coupled with their inherent chromophore characteristics enhances resonant signaling (Tassinari et al., 2021).
- Significance :
- Demonstrates the importance of intracellular structures in generating EM fields.
- Proposes microtubules as key players in orchestrating morphogenetic processes.
3. EM Fields in Embryogenesis and Regeneration
Key Points :
- Genome-wide analysis reveals conserved transcriptional responses downstream of changes in resting potential, indicating EM fields regulate gene expression (Pai et al., 2015).
- Endogenous bioelectric networks store non-genetic patterning information, enabling precise control over developmental trajectories (Levin, 2014).
- Calcium oscillations coordinate mesenchymal cell movement during feather formation, suggesting EM fields modulate gap junction networks (Li et al., 2018).
- Significance :
- Highlights the dual role of EM fields in regulating genetic and epigenetic processes.
- Offers insights into how EM fields encode positional information during development.
4. Morphogenetic Fields and Environmental Interactions
Key Points :
- Morphogenetic fields interact with environmental cues, including Schumann resonances, to influence biological rhythms and growth patterns (Ho, 2013).
- Plants exhibit structural evidence for electromagnetic resonance, using EM fields to guide vascular pattern formation (Pietak, 2012).
- Electric fields in salamanders and other regenerating species create gradients that steer molecules to healing areas (Summhammer, 2021).
- Significance :
- Explores the ecological context of morphogenetic fields.
- Suggests that EM fields may act as universal signals across species and environments.
5. EM Fields in Cellular Self-Organization
Key Points :
- Cells generate endogenous EM fields that regulate their internal and external behaviors, ensuring proper function and adaptation (Liboff, 2004; Funk et al., 2008).
- Long-range EM interactions drive protein-protein approaches, enabling selective binding and reducing randomness in crowded cellular environments (Niccolai et al., 2022).
- Stochastic resonance occurs when weak periodic signals interact with cellular noise, enhancing signal detection and processing (Kruglov et al., 2023).
- Significance :
- Explains how EM fields facilitate self-organization and adaptability in living systems.
- Proposes stochastic resonance as a mechanism for amplifying weak but meaningful signals in biology.
6. Synchronization and Coordination of Cells
Key Points :
- Networks of non-excitable cells synchronize bioelectric oscillations, forming collective patterns essential for multicellular coordination (Cervera et al., 2019).
- Gap junctional blockade induces stochastic changes in head anatomy, revealing the plasticity of bioelectric regulation (Emmons-Bell et al., 2015).
- Cellular electric fields emerge independently of DNA, carrying ontogenetic information that guides tissue formation (Wells, 2014).
- Significance :
- Emphasizes the importance of collective bioelectric activity in multicellular systems.
- Challenges traditional views by proposing bioelectric fields as independent carriers of developmental information.
7. Practical Applications in Medicine and Biotechnology
Key Points :
- Charge-balanced electrical stimulation modulates neural precursor cell migration, offering therapeutic potential for brain repair (Iwasa et al., 2019).
- Endogenous electric fields guide cell migration in vivo, providing targets for interventions in wound healing and tissue engineering (Funk, 2015).
- Bioelectric signaling regulates size in zebrafish fins, demonstrating its role in maintaining proper proportions during growth (Perathoner et al., 2014).
- Significance :
- Opens avenues for developing novel treatments based on EM field modulation.
- Encourages integration of EM principles into regenerative medicine and biotechnology.
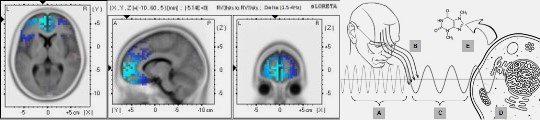
8. Morphogenetic Fields and Consciousness
Key Points :
- Morphogenetic fields can be seen as part of broader conscious fields, where form and structure reflect the physical expression of life's essence (Thorp, 2021).
- EM fields generated by living systems resonate with external environmental fields, creating nested hierarchies of consciousness (Young et al., 2022).
- General Resonance Theory (GRT) suggests that shared resonance chains allow simpler forms of consciousness to combine into more complex entities (Hunt & Schooler, 2019).
- Significance :
- Links morphogenesis with consciousness, proposing that form arises from conscious EM interactions.
- Expands the scope of EM theories to include metaphysical and philosophical perspectives.
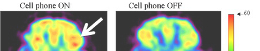
9. Heart and Brain EM Fields in System-Wide Order
Key Points :
- The heart generates the strongest EM field in the body, encoding emotional and physiological information through interference patterns (McCraty et al., 2009).
- Brain oscillations synchronize with heart rhythms, creating system-wide coherence that influences cognitive and emotional states (Ross et al., 2015).
- Heart rate variability (HRV) reflects the interaction between the heart's EM field and external geomagnetic fields, impacting overall well-being (Alabdulgader, 2021).
- Significance :
- Demonstrates the importance of the heart's EM field in maintaining systemic coherence.
- Highlights the bidirectional relationship between internal and external EM fields in regulating health and consciousness.
10. Evolutionary Preservation of EM Patterns
Key Points :
- Evolution has preserved specific EM field patterns across species, suggesting their importance in survival and adaptation (Buzsáki et al., 2013).
- Frequency-specific contributions of EM fields to cognitive performance indicate a conserved mechanism for information processing (Allen et al., 2018).
- EM fields generated by centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal roles in evolutionary processes, including symmetry breaking and field-to-protein interactions (Pokorný et al., 2011).
- Significance :
- Supports the idea that EM fields are evolutionarily conserved and essential for life.
- Links EM field dynamics with fundamental evolutionary processes like symmetry breaking.
11. Theoretical Frameworks and Future Directions
Key Points :
- Field-mediated bioelectric prepatterning models explain how EM fields regulate morphogenesis computationally (Manicka & Levin, 2025).
- Multiscale memory and bioelectric error correction mechanisms suggest that EM fields maintain stability across developmental stages (Fields & Levin, 2017).
- Novel hypotheses propose decoding EM field signatures associated with specific developmental events, such as Ca²⁺ oscillations (Smedler & Uhlen, 2014).
- Significance :
- Provides robust theoretical constructs for understanding EM-based morphogenesis.
- Calls for further research into deciphering the "bioelectric code" and its implications for life and consciousness.
References
- Manicka, S., & Levin, M. (2025). Field-mediated Bioelectric Basis of Morphogenetic Prepatterning: A Computational Study [preprint].
- Elson, E. C. (2024). Embryo Development in a Stochastic Universe.
- Levin, M. (2023). Bioelectric Networks: The Cognitive Glue Enabling Evolutionary Scaling from Physiology to Mind.
- Nunn, A. V. W., Bell, G. J. D., & Guy, W. (2022). Bioelectric Fields at the Beginnings of Life.
- Tassinari, R., Cavallini, C., Olivi, E., Taglioli, V., Zannini, C., & Ventura, C. (2021). Unveiling the Morphogenetic Code: A New Path at the Intersection of Physical Energies and Chemical Signaling.
- Thorp, K. E. (2021). Morphogenic Fields: A Coming of Age.
- Braun, E., & Ori, H. (2019). Electric-Induced Reversal of Morphogenesis in Hydra.
- Cervera, J., Pai, V. P., Levin, M., & Mafe, S. (2019). From Non-Excitable Single-Cell to Multicellular Bioelectrical States Supported by Ion Channels and Gap Junction Proteins: Electrical Potentials as Distributed Controllers.
- Tuszynski, J. A. (2019). The Bioelectric Circuitry of the Cell.
- Iwasa, S. N., Rashidi, A., Sefton, E., Liu, N. X., Popovic, M. R., & Morshead, C. M. (2019). Charge-Balanced Electrical Stimulation Can Modulate Neural Precursor Cell Migration in the Presence of Endogenous Electric Fields in Mouse Brains.
- Pietak, A. M. (2010). Endogenous Electromagnetic Fields in Plant Leaves: A New Hypothesis for Vascular Pattern Formation.
- Pietak, A. M. (2012). Structural Evidence for Electromagnetic Resonance in Plant Morphogenesis.
- Pietak, A. M. (2013). Living Energy Resonators: Transcending the Gene to a New Story of Light and Life.
- Tseng, A., & Levin, M. (2013). Cracking the Bioelectric Code: Probing Endogenous Ionic Controls of Pattern Formation.
- Guo, A., Song, B., Reid, B., Gu, Y., Forrester, J. V., Jahoda, C. A. B., & Zhao, M. (2010). Effects of Physiological Electric Fields on Migration of Human Dermal Fibroblasts.
- Levin, M. (2003). Bioelectromagnetics in Morphogenesis.
- Wells, J. (2014). Membrane Patterns Carry Ontogenetic Information That Is Specified Independently of DNA.
- Fields, C., & Levin, M. (2017). Multiscale Memory and Bioelectric Error Correction in the Cytoplasm-Cytoskeleton-Membrane System.
- Funk, R. H. W. (2015). Endogenous Electric Fields as Guiding Cue for Cell Migration.
- Cao, L., Wei, D., Reid, B., Zhao, S., Pu, J., Pan, T., Yamoah, E., & Zhao, M. (2013). Endogenous Electric Currents Might Guide Rostral Migration of Neuroblasts.
- Li, A., Cho, J.-H., Reid, B., Tseng, C.-C., He, L., Tan, P., Yeh, C.-Y., Wu, P., Li, Y., Widelitz, R. B., Zhou, Y., Zhao, M., Chow, R. H., & Chuong, C.-M. (2018). Calcium Oscillations Coordinate Feather Mesenchymal Cell Movement by SHH Dependent Modulation of Gap Junction Networks.
- Pai, V. P., Martyniuk, C. J., Echeverri, K., Cruz, S. S., Kaplan, D. L., & Levin, M. (2015). Genome-Wide Analysis Reveals Conserved Transcriptional Responses Downstream of Resting Potential Change in Xenopus Embryos, Axolotl Regeneration, and Human Mesenchymal Cell Differentiation.
- Pietak, A. M. (2015). Electromagnetic Resonance and Morphogenesis.
- Lobikin, M., & Levin, M. (2015). Endogenous Bioelectric Cues as Morphogenetic Signals in Vivo.
- Emmons-Bell, M., Durant, F., Hammelman, J., Bessonov, N., Volpert, V., Morokuma, J., Pinet, K., Adams, D. S., Pietak, A., Lobo, D., & Levin, M. (2015). Gap Junctional Blockade Stochastically Induces Different Species-Specific Head Anatomies in Genetically Wild-Type Girardia Dorotocephala Flatworms.
- Hubacher, J. (2015). The Phantom Leaf Effect: A Replication (Part 1).
- Summhammer, J. (2021). Morphology and High-Frequency Bio-Electric Fields.
- Perathoner, S., Daane, J. M., Henrion, U., Seebohm, G., Higdon, C. W., Johnson, S. L., Nüsslein-Volhard, C., & Harris, M. P. (2014). Bioelectric Signaling Regulates Size in Zebrafish Fins.
- Tyler, S. E. B. (2014). The Work Surfaces of Morphogenesis: The Role of the Morphogenetic Field.
- Cifra, M. (2012). Electrodynamic Eigenmodes in Cellular Morphology.
- Iwasa, S. N., Babona-Pilipovs, R., & Morshead, C. M. (2017). Environmental Factors That Influence Stem Cell Migration: An "Electric Field".
- Ho, M.-W. (2013). Life is Water Electric.
- Detmar, C. F. (2022). An Adaptational Theory of Consciousness.
- Keppler, J. (2021). Building Blocks for the Development of a Self-Consistent Electromagnetic Field Theory of Consciousness.
- McFadden, J. (2020). Integrating Information in the Brain’s EM Field: The CEMI Field Theory of Consciousness.
- Jones, M. W. (2016). Mounting Evidence That Minds Are Neural EM Fields Interacting with Brains.
- Khrennikov, A. (2010). Quantum-Like Model of Processing of Information in the Brain Based on Classical Electromagnetic Field.
- Wnuk, M. J., & Bernard, C. D. (2001). The Electromagnetic Nature of Life - The Contribution of W. Sedlak to the Understanding of the Essence of Life.
- Jones, M. W. (2019). Growing Evidence That Perceptual Qualia Are Neuroelectrical Not Computational.
- Hales, C. G., & Ericson, M. (2022). Electromagnetism’s Bridge Across the Explanatory Gap: How a Neuroscience/Physics Collaboration Delivers Explanation Into All Theories of Consciousness.
- McCraty, R., Atkinson, M., Tomasino, D., & Bradley, R. T. (2009). The Coherent Heart: Heart–Brain Interactions, Psychophysiological Coherence, and the Emergence of System-Wide Order.
Keywords
- Electromagnetic Fields (EMFs), Morphogenesis, Bioelectricity, Centrosomes, Microtubules, Synchronization, Regeneration, Consciousness, Panpsychism, Fractal Dynamics, Quantum Effects, Neural Precursor Cells, Gap Junctions, Epigenetic Regulation
Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 11/02/2025
↓ tables updated (Human): 27/01/2025
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 EM & Morphogenetics
EM & Morphogenetics
.
.