Electromagnetism & DNA
This biomolecule has important electrical properties and various EMF generation possibilities
DNA, the fundamental blueprint of life, exhibits not only biochemical but also electromagnetic properties, enabling it to act as a dynamic participant in cellular processes. This section explores the electromagnetic (EM) capabilities of DNA, including its resonance phenomena, signal transmission, and interaction with cellular structures. ...
By integrating experimental evidence and theoretical models, it is highlighted DNA's role as an electromagnetic resonator and its potential implications for cellular regulation, intercellular communication, and systemic coherence in living organisms.
DNA is traditionally understood as the repository of genetic information, facilitating protein synthesis and heredity. However, recent studies reveal that DNA also functions as an active electromagnetic structure. These properties suggest that DNA's role extends beyond its chemical composition, implicating it in processes such as cellular organization, epigenetic regulation, and even long-range biological communication. This section examines the emerging understanding of DNA’s electromagnetic behavior and its implications for biology.
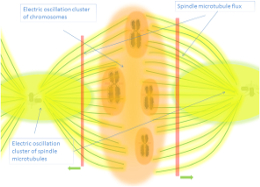
Electromagnetic Resonance in DNA: The helical structure of DNA enables it to act as a fractal electromagnetic cavity resonator, capable of absorbing and emitting electromagnetic waves. Studies have demonstrated that DNA resonates within terahertz and microwave frequencies, with sequence-dependent variations influencing resonance behavior (Savelyev et al., 2019; Guschin et al., 2018). Experimental evidence from bacterial DNA reveals resonant absorption of microwaves at specific frequencies corresponding to torsional vibrations, highlighting its role as a precise EM sensor (Ikhlov, 2022).
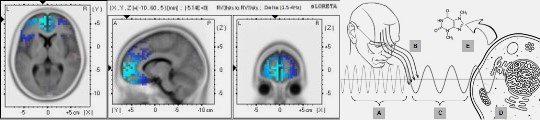
DNA emits ultraweak photons, often referred to as biophotons, which contribute to cellular communication and regulation. These emissions are influenced by DNA’s structural configuration, including its compaction and interaction with chromatin. Additionally, researchers propose that DNA acts as a helical antenna, generating and receiving electromagnetic signals that facilitate environmental sensing, intercellular coordination, and potentially transmitting genetic information.
Electromagnetic Fields in Cellular Regulation: Chromatin, the complex of DNA and proteins, generates oscillating electromagnetic fields during processes such as transcription and replication. These fields influence chromatin organization and the compaction of chromosomes, contributing to the regulation of genetic expression. DNA also exhibits properties analogous to modern antenna arrays, where nucleotide sequences act as elements within a coordinated network. This organization enhances signal coherence, enabling robust information transmission and error correction.
Furthermore, the electromagnetic properties of DNA allow it to convert energy into informational signals, guiding molecular interactions and underpinning phenomena such as epigenetic modifications and cellular adaptation to environmental cues.
Intercellular and Systemic Implications: DNA’s resonance signals propagate through microtubules and cytoskeletal structures, forming an integrated communication network that synchronizes cellular activity. The DNA-microtubule resonance hypothesis suggests a mechanism for connecting intracellular and extracellular EM signaling, contributing to tissue and systemic coherence (Petoukhov et al., 2023). Electromagnetic signaling in DNA also influences developmental processes such as morphogenesis, differentiation, and cellular spatial orientation, guided by ontogenes (specialized genetic structures).
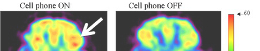
These insights have inspired medical innovations. Techniques like EM field therapy and biophoton-based diagnostics leverage DNA’s resonant properties for applications in regenerative medicine and disease treatment.
Discussion: The electromagnetic capabilities of DNA extend its role beyond being a genetic blueprint to acting as a dynamic participant in cellular and systemic regulation. DNA’s resonance properties enable it to serve as a conduit for information transfer, a mediator of coherence, and a regulator of energy dynamics. These findings challenge traditional views of DNA and emphasize the need for interdisciplinary approaches to fully understand its multifaceted roles.
Conclusion: DNA’s electromagnetic properties provide a new perspective on its function, highlighting its role in cellular communication, systemic organization, and biological coherence. Further research into these properties promises to deepen our understanding of life’s fundamental processes and inspire novel applications in science and medicine.
Keywords: DNA, electromagnetic resonance, biophotons, chromatin oscillations, bio-antenna, systemic coherence, cellular communication.
-Text generated by AI superficially, for more specific but also more surprising data check the tables below-Very related sections:
↑ text updated (AI generated): 23/12/2024
↓ tables updated (Human): 22/02/2025
Endogenous Fields & Mind
 EM & DNA
EM & DNA
.
.